How Heat sinks Are Made: Exploring Modern Manufacturing Techniques
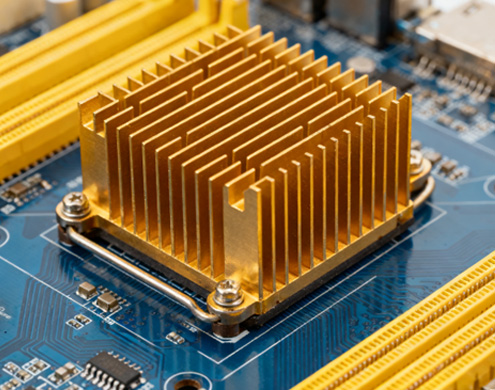
With electronic devices becoming increasingly powerful and smaller, effective thermal management has become crucial for device performance. Heat sinks, components that dissipate heat from sensitive electronic parts, have undergone significant changes in design and manufacturing methods. From traditional extrusion processes to innovative 3D printing technologies, manufacturers now have a variety of options to create efficient cooling solutions. Below, we'll delve into how heat sinks are manufactured today.
Extrusion Molding: Heat Sinks A Cost-Effective and Mainstream Process
Extrusion is one of the most common and economical processes for producing aluminum heat sinks. This process involves extruding heated aluminum alloy through a die of a specific shape to form common heat sinks fin shapes. It is highly efficient in mass production, but its limitations in the aspect ratio of fin size to spacing restrict its application in compact, high-performance equipment.
Skiving: Heat Sinks A High-Performance Alternative
The process involves slicing thin layers of material from a block of metal and bending these sheets upwards to form fins. This process produces very dense, high-surface-area fins with excellent thermal contact with the substrate. Sliced fins typically offer better heat dissipation than extruded fins and are often made of copper, as copper has better thermal conductivity than aluminum. This process is particularly valuable in space-constrained applications where optimized heat dissipation is crucial.
Casting: Heat Sinks Suitable for Complex Geometries
Casting technology enables more complex, three-dimensional heat sinks designs that are impossible to achieve in extrusion processes. In traditional casting, molten metal is poured into a mold and allowed to solidify. Modern hybrid approaches combine additive manufacturing with traditional casting, using high-precision 3D printing to create resin templates, which are then used to create metal casting molds, maintaining the cost-effectiveness of casting while providing design flexibility.
Milling: Heat Sinks Precision and Customization
Milling is a manufacturing method that removes material from a solid block to create the desired fin-like structure. While milling is generally more expensive and wastes more material compared to other methods, it offers unparalleled precision advantages, making it ideal for prototyping, small-batch production, and custom applications. Recent advancements in micro-milling technology have enabled the fabrication of extremely fine features. The use of ultrasonic vibration-assisted methods has yielded significant results in material machining, reducing cutting forces by over 20% and extending tool life.




