Heat dissipation materials and Heat sink components
Heat dissipation materials and Heat sink components
As electronic devices continue to improve in performance, installing heat-generating components requires measures to dissipate this heat to prevent malfunctions or failures. Many specialized components and materials contribute to heat dissipation, each with its own unique properties. Among these diverse heat dissipation materials, aluminum and its alloys have become a mainstream choice due to their unique advantages.
Materials used for heat dissipation components
Aluminum's Advantages: An Ideal Heat Sink Material
Aluminum's popularity in the heat sink industry stems from its exceptional physical properties. Pure aluminum boasts a thermal conductivity of 238 W/(m·K). While this is second only to copper and silver among metals, its lightweight and cost-effectiveness far surpasses copper. Aluminum's density is only 2.7 g/cm³, making it particularly important in today's world of lightweight and thin electronic devices. Aluminum alloys also offer excellent formability and can be fashioned into heat sinks of various shapes through a variety of processes. Anodizing creates a durable oxide film, enhancing corrosion resistance while also meeting the aesthetic requirements of various devices.
Manufacturing Process: A Key Determinant of Heat Sink Performance
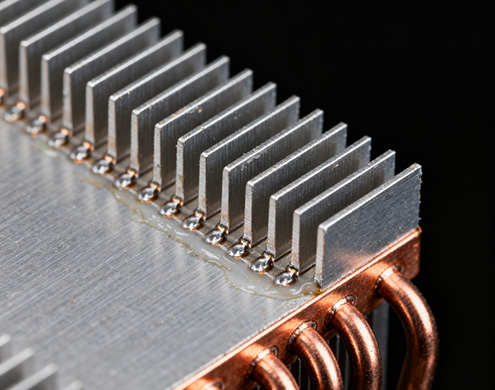
Aluminum heat sinks are manufactured using a variety of processes, each significantly impacting the performance of the final product. Extrusion is the primary process for producing aluminum heat sinks, enabling ultra-thin fins and therefore widespread use in cooling micro and medium-power devices. Cold forging is a recently emerging technology. Cold-forged aluminum heat sinks combine the excellent surface treatment properties of aluminum profiles with the ability to form complex shapes in a single step, making them considered the optimal direction for heat sink manufacturing. Die-casting is suitable for large, complex heat sinks, but die-cast heat sinks often have internal pores.
Heat Dissipation Components
Heat sinks are components designed to utilize the high thermal conductivity of heat-dissipating materials to further improve heat dissipation efficiency, such as heat pipes. Heat sources on one side of a heat sink contact a flat surface, while the other releases heat to the air. Heat sinks can be constructed of thin plates, bellows, or needles, primarily made of aluminum, copper, or ceramic. The greater the surface area available for heat transfer, the better the heat dissipation performance.
A heat pipe is a tubular heat dissipation component, usually made of copper. The principle is to remove heat by repeated evaporation cycles. The circulation of the liquid is rapid and continuous. Compared with heat sinks or graphite sheets, the heat dissipation performance of heat pipes is much better.




